Case of the Week #550
Akdeniz University, School of Medicine, Antalya, Turkey
Posting Dates: January 1 - January 14, 2022
Case Report: A 23-year-old woman (G1P0) was referred to our clinic for suspected fetal anomalies at the 25th week of gestation. First trimester screening test risk for Down syndrome was low. Fetal biometry revealed a large for gestational age fetus ( >99% percentile). Main ultrasound examination findings are depicted below:
View the Answer Hide the Answer
Answer
We present a case of Noonan syndrome.
Our ultrasound findings show:
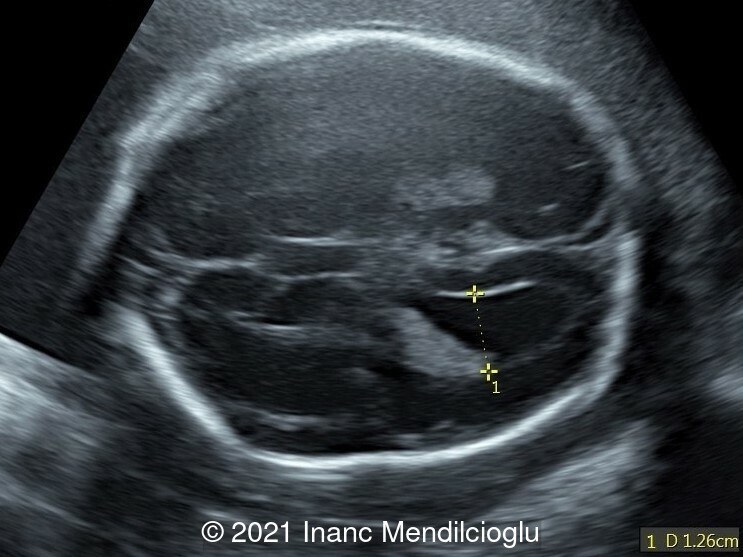
- Image 1 Ventriculomegaly
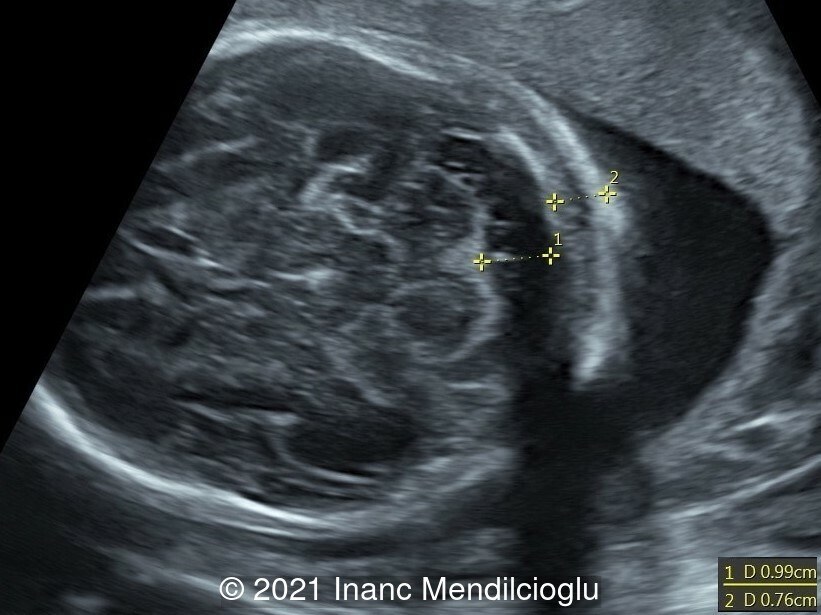
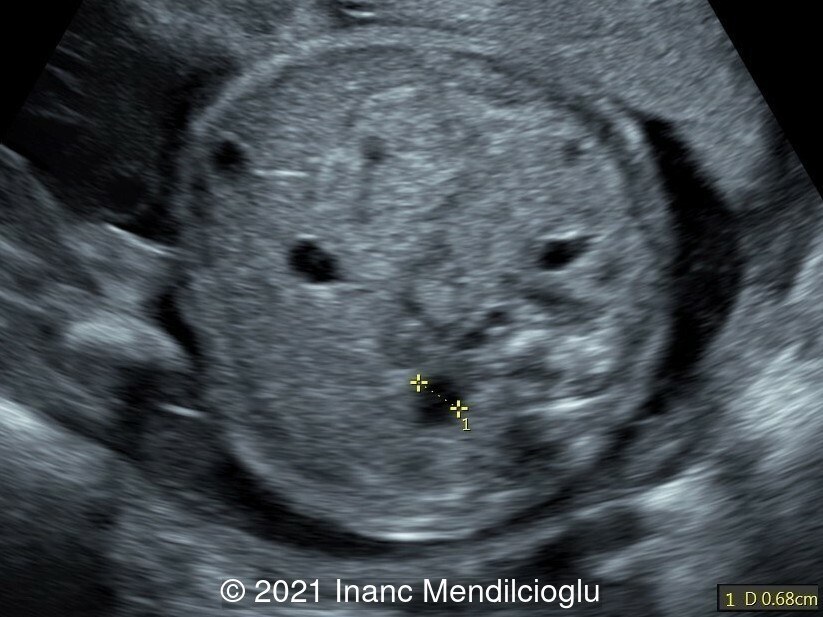
- Image 2 Increased nuchal fold
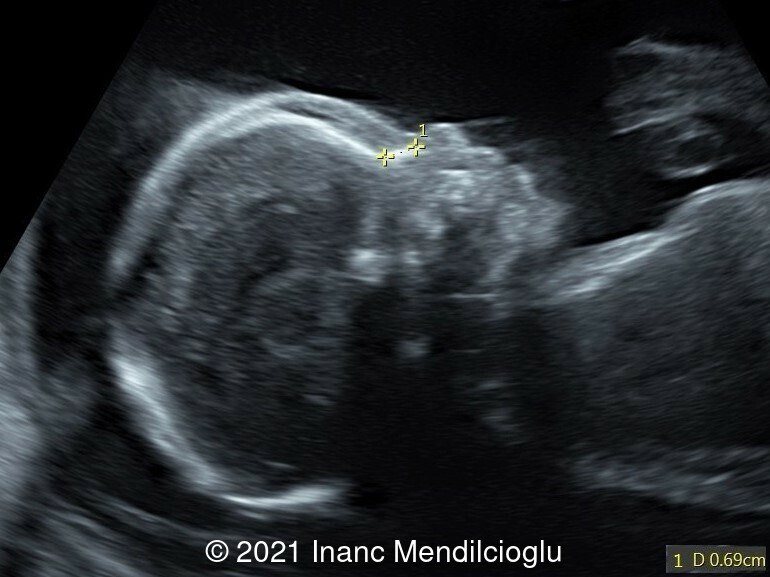
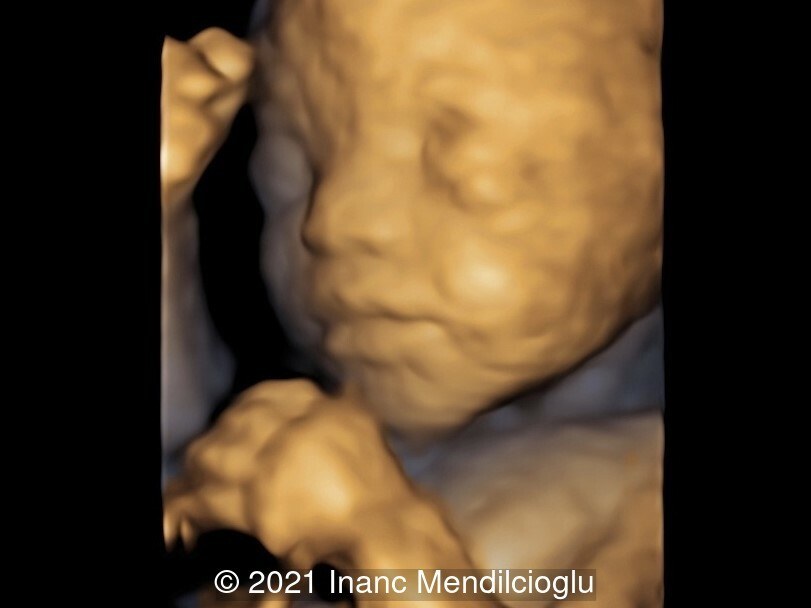
- Image 3,6 Prominent forehead, depressed nasal bridge
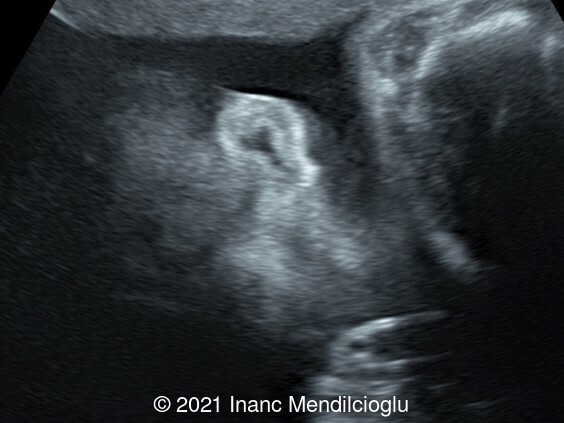
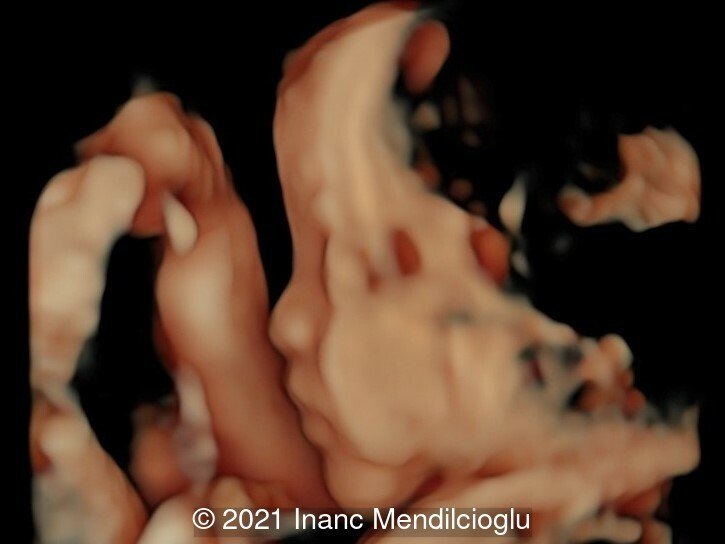
- Image 4 Low-set, posteriorly rotated ears
- Image 5 Hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures
- Image 7 Renal dilatation
- Video 1-2 Inlet ventricular septal defect
A female neonate was born at term with APGAR scores 9 and 10 at 1 and 5 minutes. Height was 50-75th percentile (51cm) and head circumference was 75th percentile (37cm). On examination, the infant was hypotonic with dysmorphic facies, wide philtrum, low-set, posteriorly rotated ears, macroglossia, short and webbed neck, and low hairline. Neonatal ECHO showed an inlet ventricular septal defect.
Whole exome sequencing revealed RAF1 mutation consistent with Noonan syndrome. Parents did not have any mutation related to Noonan syndrome.
Discussion
Noonan syndrome is a rare genetic disorder, usually autosomal dominant, and presents with short stature, facial dysmorphism (broad forehead, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, a high-arched palate, and low-set, posteriorly rotated ears). Pulmonary valve stenosis and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are the most common forms of cardiac disease. Additionally, atrial septal defects and ventricular septal defects are also observed. Other frequent findings are skeletal defects (chest defects), webbed neck mental retardation, cryptorchidism, and bleeding diathesis. [1]
The most common mutation is PTPN11 (12q24.13), seen in 50% of cases. Other mutations identified are SOS1 (2p22.1), found in 15% of cases, RAF1 (3p25.2), RIT1 (1q22) and LZTR1(22q11.21). [2]
Prenatal findings associated with Noonan syndrome are increased nuchal translucency, cystic hygroma, ascites, polyhydramnios, cardiac anomalies, and dysmorphic facial features. Prenatal diagnosis is possible on chorionic villi or amniotic fluid. [2]
References
[1] McKusick VA, O'Neill MJF. "Noonan Syndrome 1; NS1. # 163950." OMIM. https://omim.org/entry/163950, publish date 06/1986, last update 11/2020.
[2] Verloes A. ” Noonan syndrome.” Orphanet. https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?Lng=GB&Expert=648, Last update 04/2020.
Discussion Board
Winners

Fatih ULUC Turkey Physician

Umber Agarwal United Kingdom Maternal Fetal Medicine

Cem Sanhal Turkey Physician

Philippe Deblieck Germany Physician

Ta Son Vo Viet Nam Physician

Akmaral Medetbekova United States Physician

Murat Cagan Turkey Physician

Umutcan KAYIKÇI Turkey Physician